Project Finance Modeling Building Skills for Infrastructure Finance Careers
Project Finance Modeling: Building Skills for Infrastructure Finance Careers
Introduction to Project Finance Modeling Building Skills for Infrastructure Finance Careers
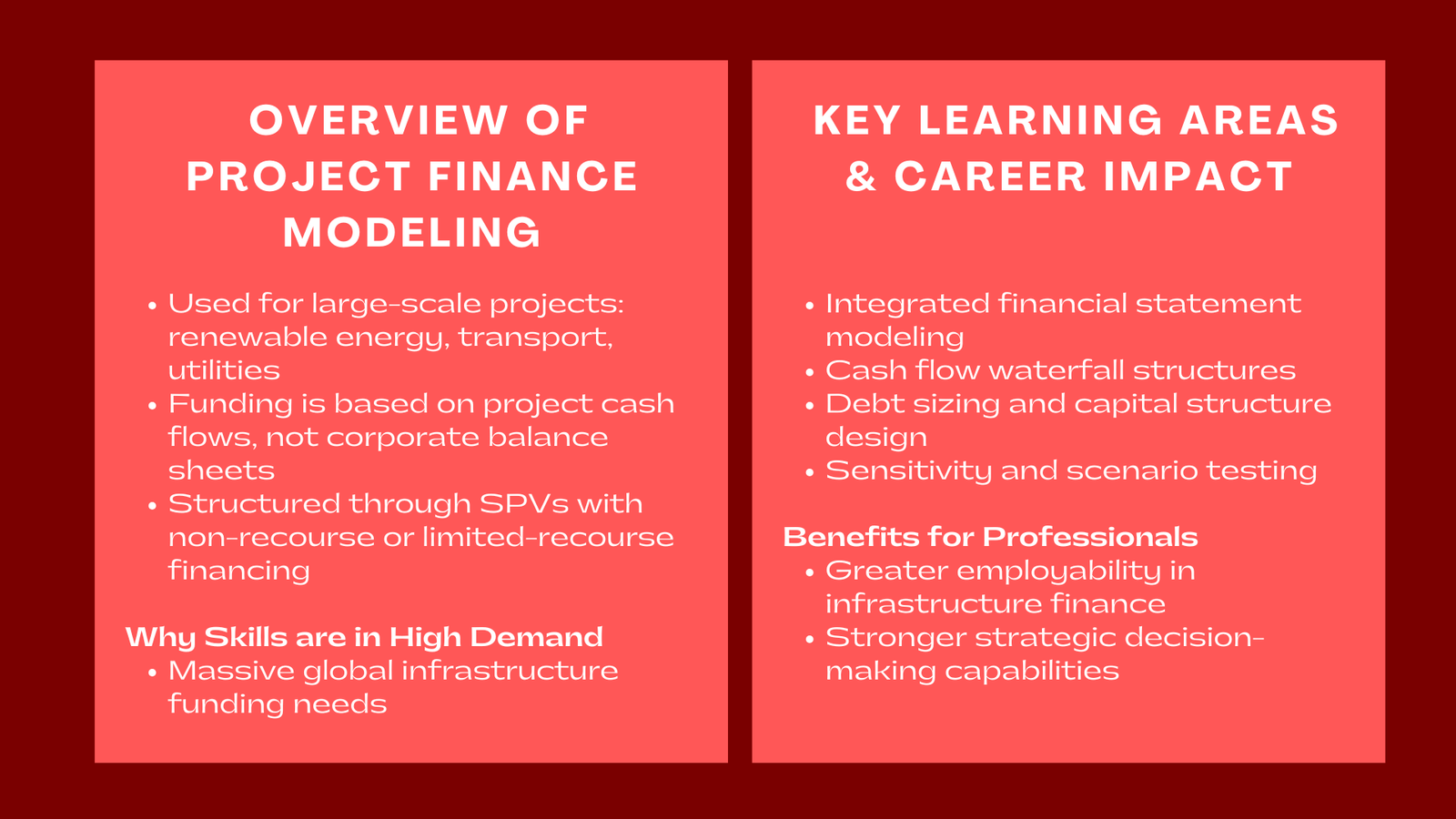
Project finance is one of the most vibrant and niched areas of corporate finance in the world of large-scale infrastructure and capital-intensive projects. Project finance structures can be used to develop huge projects in renewable energy plants, toll roads, airports and utilities of the people without straining a balance sheet of the company.
The core of this field is the project finance modeling — an important skill that enables practitioners estimate the viability of investment, design debt and equity as well as risk management over the life of a project. With the growing need of infrastructure investment in the world, Project Finance Modeling: Building Skills to Infrastructure Finance Careers has become an imperative course of learning among professionals in the finance field who are interested in expanding their positions to this fast developing sector, especially those seeking advanced financial modelling and valuation training in Singapore to elevate their expertise in the infrastructure finance industry.
This is a work of understanding Project Finance.
Project finance is a financing technique of huge projects founded on the anticipated future cash flows of the projects instead of the balance sheets of the sponsors. It normally brings in various stakeholders, among them developers, lenders, investors, and government bodies. All the participants have some risks and rewards, which are organized in a complicated network of agreements and financial tools.
Project finance, as compared to corporate finance, separates the revenues and expenses of a project into a special purpose vehicle (SPV), rather than basing the funding on the assets of the company. This non-recourse or limited-recourse structure will enable financiers to evaluate the performance of the projects by themselves so that cash flow generated by the project can determine the payment.
Due to this complexity, those in the project finance profession require or should have good technical, analytical, and modelling skills-skills, which can only be acquired after undergoing intensive, practical training.
Project Finance Modeling What Is It?
Project finance modeling is the development of dynamic financial model to assess viability of projects, profitability, and sustainability of infrastructure projects. The models are used to determine the potential returns and risks by investors, lenders and sponsors as a tool to make decisions.
A model is built to give us an insight into the key metrics like:
- Projected cash flows
- Debt service coverage ratios (DSCR)
- Internet rate of return (IRR) and net present value (NPV).
- Revenue/cost/interest rate sensitivity analysis.
- Equity and debt holder risk-adjusted returns.
Through learning modeling skills, finance specialists will be able to model various situations- trying to determine how delays, cost overruns or demand changes can impact the performance on the balance sheet.
The reason why Project Finance Modeling Skills Are in Demand.
The surge in global infrastructure void, as well as the shift to a sustainable energy and digital infrastructure, have led to a great supply of project finance professionals. Both governments and private investors are in need of experts who would create, assess, and fund projects with all the accuracy and responsibility.
To finance professionals, the development of modeling skills has a number of important benefits:
- Increased employability: Employers in investment banks, infrastructure funds and advisory firms appreciate candidates who are able to develop strong models to aid deal structuring.
- Better financial understanding: The modeling skills allow the professionals to determine the risks of the project and returns and reinforce the recommendation of investments.
- Career versatility: Project finance expertise allows a professional to enter the fields of renewable energy, utilities, transport, and public-partner companies (PPPs).
- Strategic decision making: The knowledge of the financial mechanics of operating large-scale projects enables professionals to affect the strategic and policy-level decisions.
Basic Building Blocks of Project Finance Modeling.
Integration of Financial Statements.
Income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements are the blocks upon which any project finance model is built. The learners need to learn how to interconnect these statements in a logical way in order to show the financial aspects of the project in the long run.
Debt and Equity Structuring
One of the biggest components of project finance modeling is to come up with the optimum capital structures. This involves the computation of debt service schedules, interest payments as well as equity contributions whilst ensuring the desired coverage ratios.
Cash Flow Waterfall
The cash flow waterfall establishes the sequence of cash flows distribution of the project; usually the revenues are allocated to operations, debt service, reserve accounts and finally the equity distributions. This concept is of paramount importance in order to make sure that these models reflect the lender and investor priorities.
Risk and Sensitivity Analysis.
By using scenario and sensitivity analysis, professionals will experiment to evaluate the impact that the key variables, such as inflation, tariffs, or exchange rates, have on the project outcomes. This helps the stakeholders to project the financial risks and make reasonable decisions.
Financial Returns and Valuation Metrics.
Other performance measures that are used in modeling include the IRR, NPV, payback period and the project yield. Such measures allow calculating the viability and appeal of a potential investment.
The worth of organized training in the project finance modeling.
Most finance professionals have simple Excel or financial analysis skills, but to model project finance they have to have a more advanced and technical degree of expertise. Formal training is an effective model of training whereby, based on real-life projects, case studies, and guided model-building activities, learning takes place.
These programs usually entail courses on financial structuring, risk allocation and infrastructure valuation- skills that are very essential in successfully working in an infrastructure investment teams. The participants are taught on how to create flexible and transparent designs that can respond to the changing project parameters and investor needs.
The training course that is organized correctly shortens the distance between theory and practice and helps to bridge the gap between the theoretical knowledge gained in a classroom and the practice in the field.
How Professionals Benefit from Specialized Modeling Training
For individuals seeking to build long-term careers in infrastructure finance, training in hands-on project finance modeling courses for infrastructure professionals delivers measurable career benefits. These courses provide participants with the ability to:
- Develop complete project finance on its own.
- The knowledge of debt sizing, interest rate modeling and refinancing.
- Carry out extensive scenario analysis of various structure of projects.
- Report modeling outputs efficiently to the top management and investors.
- use best practices of transparency and auditability on financial models.
Similarly, organizations benefit from enrolling their teams in advanced infrastructure project finance modeling training for corporate finance teams, enabling their employees to support transaction execution, due diligence, and financial decision-making with accuracy and consistency.
Companies enhance their capacity to analyze investment opportunities, negotiate the terms of funds, and control the performance of the project at different phases by training their financial professionals with the specific skills.
The Technology in the Project Finance of the Modern Era.
It has changed the way project finance teams work, with the emergence of digital modeling platforms, state-of-the-art analytics and cloud-based collaboration tools. Real-time data, scenario modelling and automatic updates can now be included in financial models–enabling the stakeholders to assess the viability of projects in real-time.
These digital tools are becoming more and more integrated into training programs, and professionals are taught how to use technology to create quicker and more precise financial models. This technological dexterity does not only increase productivity but also better transparency and communication among the investors, lenders and project sponsors.
Infrastructure Finance Careers.
Project finance modellers Professionals with skills in project finance modelling are in high demand in the following types of employment:
- Project Finance Analyst/associate.
- Infrastructure Investment Associate.
- Financial Modeling Consultant.
- Renewable Energy Finance Specialist staff.
- Debt Adv Pro Corporate Finance.
These roles are found in investment banks, infrastructure funds, multilateral development banks and advisory firms. The knowledge acquired at project finance modeling schooling enables individuals to work on some of the most influential infrastructure projects in the world- sustainable power generation or transport and information and communication.
The Future of Project Finance Education.
With the shift of infrastructure investment to the path of sustainability and digitalization, the educational focus of future project finance training is likely to lean towards ESG integration, green financing models, and climate risk modeling. The professionals will be required to comprehend the impacts of the environmental and social aspects on the cash flow of projects and how they influence the project financing.
Moreover, the increasing application of the artificial intelligence and predictive analytics will further automate the project assessment and the prediction of risks. Those finance professionals who would still upgrade their skills in these new fields will be out at the forefront of innovation in infrastructure finance.
Conclusion
Infrastructure investment success is based on project finance modelling. It enables the finance professionals to be precise in analyzing the risks, structure of capital, and maximize the performance of the project.
With the help of the Project Finance Modeling: Building Skills to a Career in Infrastructure Finance, both individuals and organizations can be in a position to succeed in one of the most critical segments of the world economy. As sustainable growth is further influenced by infrastructure, individuals with well-developed modeling and analysis capabilities will be the defining factor in driving the projects that will drive the world in the future.