Master Forecasting Budgeting and Cash Flow Modeling Skills
Master Forecasting Budgeting and Cash Flow Modeling Skills
Guide to Master Forecasting Budgeting and Cash Flow Modeling Skills
Businesses in the contemporary financial environment are required not only to be lightly on their feet but also to be as accurate as possible in their financial planning. Forecasting, budgeting, and cash flow modeling can be discussed as three of the most fundamental elements that help organizations to achieve this. Although they are closely related, each one plays a specific role in the decision making process to guide businesses and see that the financial resources are utilized wisely.
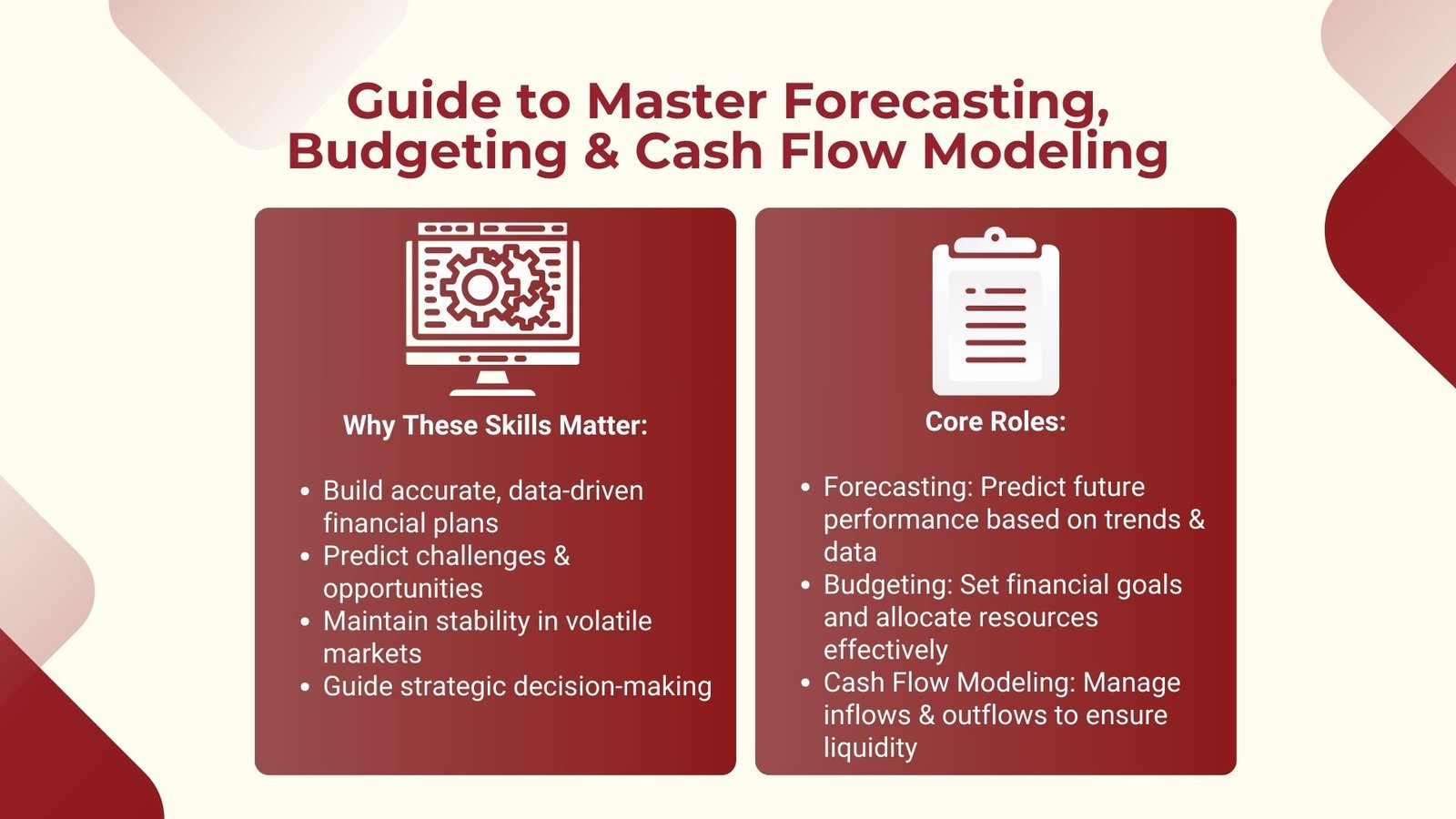
Forecasting is concerned with predicting future performance, using current trends, and previous records, budgeting concerns setting out financial aims and constraints with the intention to regulate the expenditure, and cash flow modeling is concerned with projecting capital inflow and outflow within an organization so as to have liquidity. Collectively, the tools enable financial analysts, executives, and decision-makers to gain a clear picture of how healthy the business is financially and where the business is headed towards in terms of growth.
Knowledge of the concepts is vital to the analyst who is required to do proper projection to the managers who must plan operations effectively and the business owners who are keen to ensure that profitability is not threatened. With the help of forecasting, budgeting and cash flow modeling, professionals will be able to better predict challenges and opportunities and sustain financial stability in the volatile markets. What all these processes have in common and what is truly valuable is the combination of the process, which will allow a certain informed decision to be made which will no longer be reacting to changes but be strategically directing the future.
The Role of Forecasting in Financial Planning
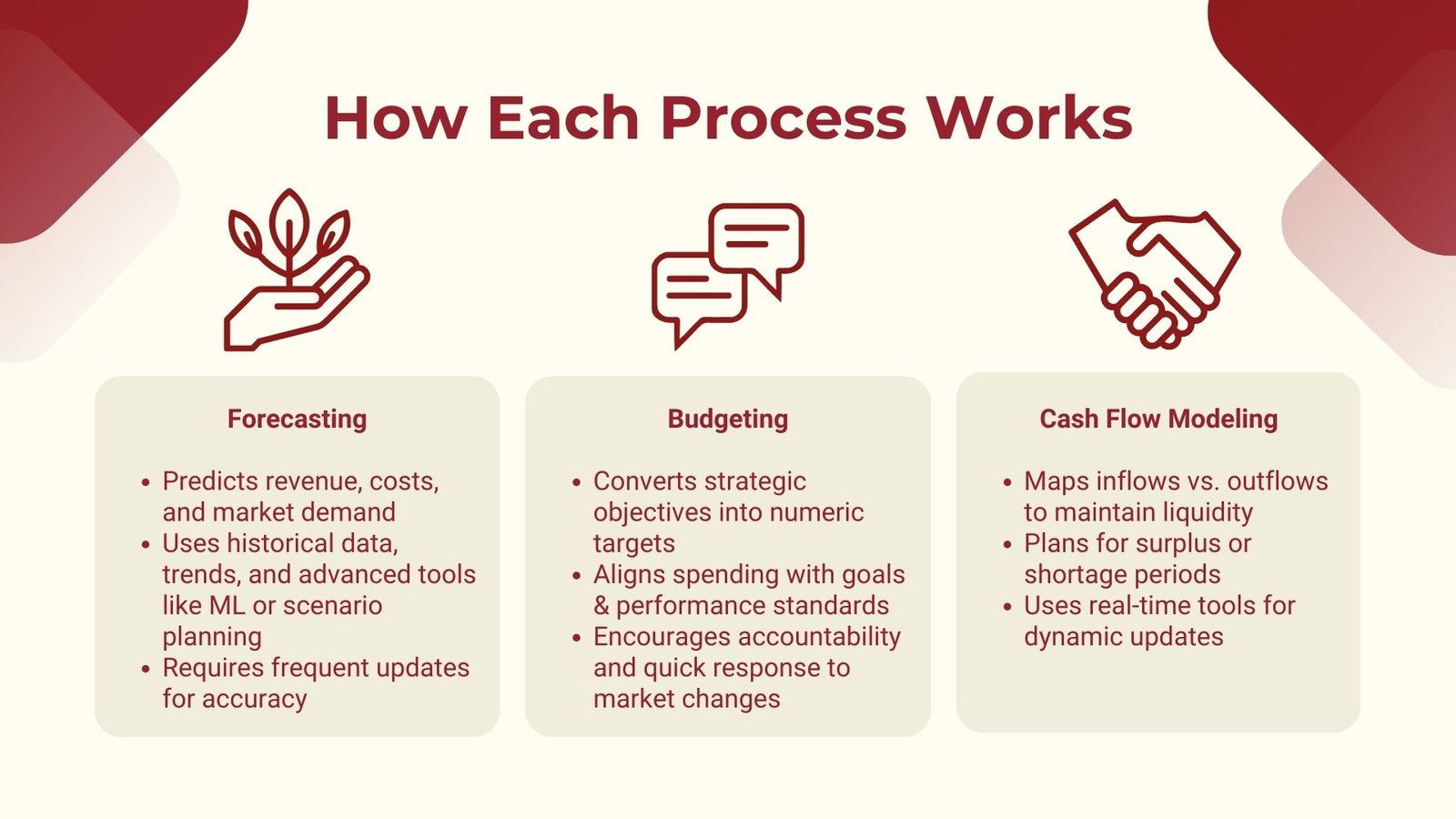
Prediction is the exercise of forecasting the financial future with past findings, present performance measures and the anticipated market. It enables businesses to make plans of different situations and be able to change strategies. Practically, forecasting may be categorized in various ways including short term projection, which can be over a period of a few months or even long term, which can go on several years. Revenue trend, cost trend, market demand fluctuations and macroeconomic effects on the business are some of the aspects that are predicted using forecasting as a financial analysis process.
The proper forecast is constructed upon well performed data analysis and exposure to reality. An illustration of this would be in sales forecasting, a firm may examine past seasonal sales and consider the economic environment, and the future change in the product lines or prices. There may also be advanced techniques of forecasting that rely on statistical models, machine learning or scenario planning to perfect the forecast. They may be more accurate especially where the dataset is large or the market is complicated.
Forecasting is not a discrete exercise and requires continuous updates depending on the variations in the conditions. Inaccurate or old forecasts may result in bad decisions, loss of opportunities or liquidity difficulties. That is why rolling forecasts used at most organizations are frequently updated with new information as opposed to the annual projections only.
Budgeting as a Strategic Control Tool
Although forecasting tells what may occur, budgeting defines the program of what the organization desires to attain in short of funds. A budget is the forecasted revenues, costs and capital allocations over a given time frame which is usually one year in fiscal terms. It includes converting strategic objectives to numeric values, making sure that departments and teams are provided with a financial performance target, and matching resources and strategies that lead to the business priorities.
A good budget is both a planning tool, and a control tool. It makes sure that expenditure is in line with organizational goals, assists in setting priorities in investing, and enables managers to compare performances to previously set standards. An example is that at mid-year when sales levels are underperforming as compared to their estimates then the budget will help in corrective actions like slowing on discretionary expenses or changing marketing tactics.
Budgeting has some component in motivation of the teams since accountability and performance can be sparked through set financial objectives. A budget, however, needs to be one that is flexible so that it can withstand the variance towards something unexpected. This is whereby the concept of flexible budgeting or zero-based budgeting may be useful so that the organisations can redeploy their resources swiftly in the wake of the market changes.
Combining budgeting and forecasting acts as a feedback mechanism where the real performance may be matched with the planned and predicted performance levels making strategy adjustments and decision making simpler.
Cash Flow Modeling and Its Importance
Cash flow modeling is aimed at indicating the in and out flow of cash in an organization. Although profitability is a major player in business, the company can still be on its knees when it does not have enough cash to cover short term liabilities. The purpose of cash flow modeling is to provide adequate liquidity to the companies to meet operational, as well as their debt and investment commitments. Professionals can enhance these skills by enrolling in a Cash flow forecasting and liquidity management course.
The operation entails the mapping of all the anticipated cash inflows, which could be sales revenue, loan proceeds, and sale of assets against anticipated outflows, which could be payroll, supplier payments, taxes, and capital expenditures. Such models are frequently used by analysts to determine times of surplus cash or shortage of cash in order that the business can be planned around this.
As an example, a seasonal business may model the cash flow to enter into months with low revenue knowing that cash reserves or means of financing are available to cushion the periods. In heavily capital-intensive industries, it is important to accurately project the cash flow to make sure that substantial investments do not cause the disruption of the operations liquidity.
The modernity of financial tools and computer software programs enhanced the active cash flow modeling, as it is possible to update the working process in real time depending on the fluctuations in sales, expenses, or funds. Together with forecasting and budgeting, the model of cash flow provides the decision-maker with an overview of the financial strength and elasticity of the company.
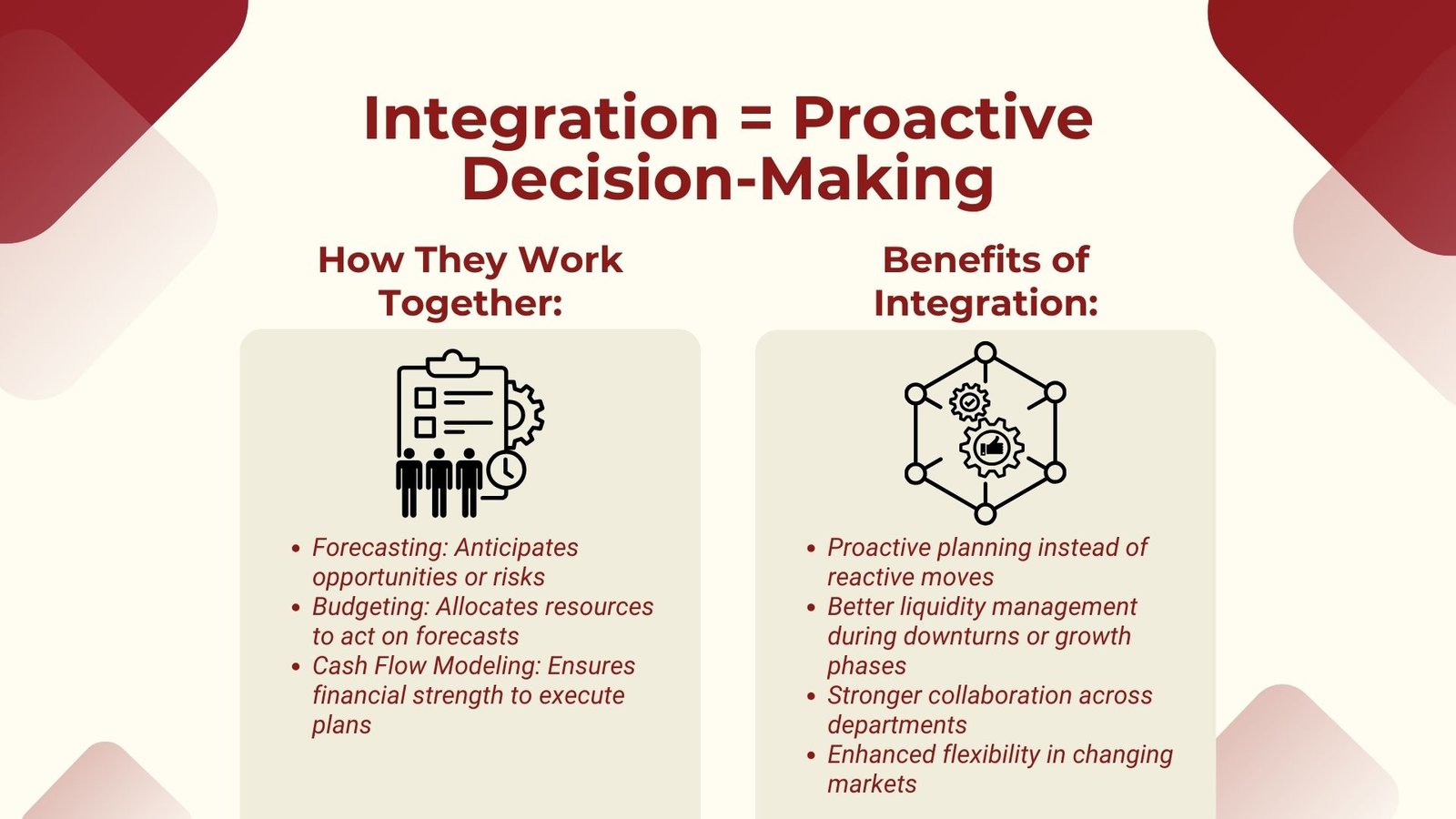
Integrating Forecasting, Budgeting, and Cash Flow Modeling
Although they have various functions, they are merged in effectiveness by integration. Forecasting gives an idea of what may happen in the future, budgeting will dictate how to go about in the circumstances created by the forecasting and cash flow modeling will automate the accounting to provide the financial strength to act upon the budgeting. Professionals can enhance their skills through Public finance risk management training Singapore.
An example is that a forecast may suggest that a market will undergo a downturn, so changes in the budget to minimize expenditures and save cash may occur. The cash flow modeling would then determine whether these changes are adequate so as to sustain the liquidity in the downturn. On the same note in case the forecasts dictate that there is a high chance of growth opportunity, the budget may set aside funds to grow as well as cash flow projection may give finance assurance without compromising operational stability.
Companies that have merged such processes in an effective manner are able to be proactive as opposed to reactive. They are able to accommodate external variations promptly, make good cash balances and have a stable investment with security. Via this integration, there would be an improved communication between the departments since the data involving the finance information would form a common denominator in the operational and strategic decisions made.
Building a Strong Analytical Foundation for Future Success
The success of forecasting, budgeting and cash flow modeling would greatly rely on data quality and level of analysis of the people involved. Enterprises are compelled to make certain that the financial information is appropriate, time-real, and pertinent. Also, the decisions should not be made on what is observed on paper. Decision-makers must comprehend the assumptions and risks that accompany the figures.
It can considerably enhance information accuracy and strategic importance through the use of advanced analytics, financial modeling methods and scenario planning. As an example, a business can be prepared to face the worst scenarios by running stress testing on cash flow models to test the business in a number of different economic conditions. In the same manner, introducing sensitivity analysis in forecasts may indicate how fluctuations in some key parameters, i.e., interest rates or customer demand may affect financial performance.
The eventual target is to establish a financial planning procedure which is intense but also flexible. In such times of diversity in the market environment, changes in regulation and changing customer expectations, the competitive advantage of the companies capable of predicting change and adapting its plans within a short span of time is an undoubtedly noticed advantage.
Conclusion
Finally, forecasting, budgeting and cash flow modeling are the skills that every organization should master in order to be able to make its way through the intricacies of the modern financial landscape. The components have a unique but interrelated role: forecasting gives the view of the future trends and possibilities of the market, budgeting will give the translation of strategic goals into financial plans, and cash flow modeling will guarantee liquidity and the ability to operate. When combined successfully, the processes enable businesses to make wise decisions to proactively respond to the changes in the market and to tap efficiently the financial resources available.
These tools are used practically to go beyond number-crunching. Forecasting involves constant review of information, patterns and assumptions in order to predict challenges and opportunities. Budgeting is not only an aspect of planning, but also a strategic tool of control that balances resources with the organization priorities and drives performance. Both complement each other, as cash flow models can project both inflows and outflows of capital, indicate times of excess or deficit, and make sure operations and investments remain financially viable.
Importantly, the true value of these processes lies in their integration. When forecasting, budgeting and cash flow modeling are integrated, organisations are no longer reactive in decision-making, but instead they are proactive in terms of their strategy and at the same time the organisation maintain its financial stability as it looks into new opportunities in the growth.
Companies that develop robust analytical backgrounds, exploit quality data, and implement highly analytical modeling methods can be better prepared to face unknown events, can efficiently allocate resources and performance can be made to be sustainable. Finally, these skills allow mastering the profession and can provide the opportunity to organize the company strategically, increase financial strength, and successfully achieve success in the competitive and dynamic market.