Startup and SaaS Financial Modeling Forecasting Valuation and Job Roles
Startup and SaaS Financial Modeling: Forecasting, Valuation, and Job Roles
Introduction to Startup and SaaS Financial Modeling Forecasting Valuation and Job Roles
Financial clarity is vital in the large-paced environment of companies and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) business. Financial models help entrepreneurs, investors and finance professionals to understand business performance, fundraise and estimate scalability. In contrast to conventional businesses, SaaS and startups are recurring revenue-based and fast-growing businesses, which can only be forecasted with specific methods.
The Startup and SaaS Financial Modeling can help professionals convert raw operational data, including Churn, Customer Acquisition Cost, and lifetime value into actionable information. Regardless of seed-stage startups or established SaaS companies, these models are the basis of capital raising, valuation and strategic decision-making. Through startup financial modelling training Singapore programs, founders and analysts can better support scalable and sustainable startup growth using data-driven financial insights.
The significance of Financial Modeling in Startups and SaaS Companies.
Financial modeling in startups and the SaaS model can not only be reduced to spreadsheet generation but rather to an activity in which the uncertain futures will be turned into quantifiable expectations. These models are used by founders and chief financial officers to approximate revenue growth, control burn rates, and make sure that funding rounds are timed properly.
Financial models are specifically essential in SaaS since the business concept of subscription requires recurrent flows of revenues as opposed to a single sale. This brings a new type of financial dynamics – it needs models that reflect retention rates, customer lifetime value (LTV), and annual recurring revenue (ARR).
This is not aimed at having an accurate view of what lies ahead but to establish a flexible structure that enables the businesses to test the assumptions, adjust the forecasts, and strategize capital assignment effectively.
Basic Building Blocks of a Startup and SaaS Financial Model.
An organized business model of a startup or SaaS business will usually be composed of multiple elements:
- Revenue model: Determines the method the company uses to get revenues, be it the subscriptions, freemium plan or transaction fees.
- Expense forecast: It contains operating costs of salaries, marketing, hosting, and R&D.
- Customer metrics: Customer first metrics (CAC), customer churn, and lifetime value.
- Cash flow statement: Projects fund and liquidity requirements with time.
- Valuation analysis: Determines the estimation of the company value using multiples of the revenue or discounted cash flow (DCF) models.
Collectively, these factors give a wholesome image of financial well being, as it assists the stakeholders with analyzing the growth prospects and funding needs.
The Exceptional SaaS Revenue Forecasting.
Repeating Revenue and Growth Measures.
SaaS companies are more successful because they function on recurrent subscriptions as opposed to traditional business which relies on single transaction. The model should hence concentrate on the Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) as the most important indicators of financial performance.
Certain revenue forecasting in SaaS also takes into account the churn (customers leave) and expansion revenue (upsells and cross-sells). Proper forecasts of these measures can spell out between a sustainable growth and a cash burn.
Trends in Retention and Cohort Analysis.
SaaS financial models frequently use cohort analysis – following cohorts of customers as they stay with a company to determine retention rates and customer lifetime value. This gives an idea of how product changes, price adjustments or marketing can affect the long term revenue.
Through measurement of user activity and revenue stability, analysts are able to determine the most important levers to increase growth and profitability.
Startup Financial Modeling Funding and Valuation.
Financial modeling is vital in raising funds in the case of startups. Shareholders want to see transparent data-driven forecasts that show them a way towards profitability. Pre-money and post-money valuations are calculated using models to allow founders to succeed in negotiating the size of an equity stake.
- The valuation methods commonly used to value startups are:
- Similar company analysis (CCA): Comparing similar companies.
- Venture capital approach: Calculating exit valuation and discounting it.
- Revenue multiples: Multiplication of industry multiples (e.g. ARR multiple) with projected revenues.
An adequately prepared model enables founders to explain their assumptions of valuation and match expectations with prospective investors.
Incorporating the Key SaaS Metrics into the Model.
A SaaS financial model is as accurate as it is able to be in terms of adapting operational metrics. These include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total expenditure incurred by the marketing and sales to acquire a new customer.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): This is the value of revenue anticipated to be received by a customer prior to churn.
- Churn Rate: This is the loss rate of customers in a particular time frame.
- Gross Margin: This is a representation of profitability or profitability following hosting and support costs.
- Payback Period: It is the time required to break even on acquisition cost to the customer income.
Awareness of such measures would enable financed teams to grow sustainably and retain investor trust.
Developing Analytical and Strategic Skills by training.
Any professional seeking to work in startup or SaaS finance should have specialized analytical abilities that are a combination of accounting, data mining, and strategic vision. Enrolling in startup financial modeling and forecasting courses for SaaS professionals helps participants build hands-on experience with real-world data and case studies.
Such programs normally instruct on how to:
- Build dynamic revenue and cost models.
- Study repetitive income and subscriptions.
- Carry out sensitivity analysis/scenario planning.
- Undertake valuation on SaaS-specific multiples.
- Prepare investor dashboard and presentations.
This kind of training provides professionals with technical and commercial knowledge that they need to serve as managers in high-growth, data-driven companies.
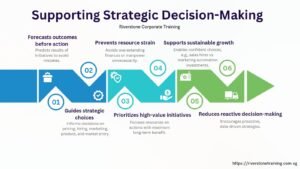
Financial Modeling Strategic Decision Making.
Financial models are not a limited instrument of investors, they can also be internal decision-making instruments. Using their models, startups test their pricing strategies, assess marketing ROI and scale operations.
Financial models in the SaaS business are used to assist management with the effect on the churn and LTV of the product upgrades or price changes. This helps the leadership teams to match the strategic objectives and the financial reality so that growth would be ambitious and real.
Using Technology and Automation in Financial Modeling.
Financial modeling has developed further than the traditional spread sheets. Forecasting is now automated using tools like Python, Power BI and cloud based analytics platforms to be able to visualize data in real time.
Many SaaS finance teams integrate their accounting and customer data into modeling software to create real-time forecasting systems for SaaS startups. These systems keep on updating measures such as ARR, churn, and gross margin, where leaders are able to make informed decisions quicker.
Automation keeps time, but minimizes human error, as well: it is important to make sure that models are accurate as the business grows.
Startup and SaaS Financing Career Opportunities.
With the continued dominance of technology companies in the world economy, finance professionals who have the skills of SaaS modeling are needed. Common job roles include:
- Financial Analyst (SaaS/ Startup): Designs and develops budget models and valuation models.
- FP&A Manager: Manages overall forecasting and scenario plans of the company.
- Investment Analyst (Venture Capital): Studies start ups to make investment choices.
- Finance Business Partner: Works with the sales and operations teams to align the growth and finance.
- Head of Finance or Startup CFO: Head of capital raising, investor relations, and long term strategy.
Such jobs need technical modeling skills as well as strategic communication skills.
The role of Financial Modeling in Career Development.
Learning how to start up and SaaS model would create opportunities to various positions within the startup world – both VC-backed startups and tech giants in the world. Financial experts who are capable of analyzing customer information, predicting growth and dealing with expectations of investors have a clear edge in competition.
Through analytical rigor and business wisdom, the professionals will emerge as the most important decision-makers to the companies, aiding them in uncertainty and scale navigation.
Conclusion
Successful startups and SaaS is all about financial modeling. It gives founders, investors and finance professionals the ability to make data-driven decisions in a world characterized by extreme change and innovation.
Through the knowledge gained in Startup and SaaS Financial Modeling: Forecasting, Valuation, and Job Roles, individuals are able to convert complex measures into straightforward financial plans- the disconnect between the analysis of the numbers and the implementation of the strategy. In a world where technology is the way to grow, the future of business and finance will be based on those well able to model technology right.