Best e commerce Financial Modeling Singapore Building simple and accurate
Best e commerce Financial Modeling Singapore building simple and accurate
Introduction: Why e commerce Financial Models Are Essential
E‑commerce business Singapore ventures are conducted in a very competitive setting where the consumer behaviors, the cost of marketing, and logistics change quickly. E-commerce venture financial modeling is invaluable in comprehending how it gets profitable and cash flow statement of e commerce, and in making future forecasts. Intensive model enables business starters, investors, and managers to undertake decisions, evaluate risks and allocate resources reasonably.
E-commerce is experiencing the peculiar challenges of the vague cost of customer intake, fluctuating stock requirements, as well as dynamic pricing strategies as opposed to traditional retail. Financial models help businesses to plan their way to expansion and optimize the organization as well as present value to their investors through conversion of these complex variables into actionable insights.
 Revenue Modeling: e commerce financial modeling Singapore Understanding Your Sales Drivers
Revenue Modeling: e commerce financial modeling Singapore Understanding Your Sales Drivers
Mapping revenue stream is the e-commerce financial modelling first stage. Other aspects which affect revenue include:
Traffic and Conversion Rates: Visitors and the ratio of people that buy the product.
Average Order Value (AOV): Instructions How much customers pay per order.
Repeat Purchase Rate: The rate of returning customers.
What will be important: Representing various growth conditions allows business to project revenue at various conditions, predict effects of seasonality, and also have realistic sales projections.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and Gross Margin
COGS information is necessary to e-commerce profitability. It comprises costs of the product, shipping, packing as well as the fulfillment. A scenario to gross margin Revenue less COGS model forecasts the pricing strategy and evaluates the efficiency in which the business is converting revenue into profit.
Why is it important: The clear vision of the margins enables the e-commerce managers to optimize their suppliers, negotiate more favorable rates, and determine what kinds of products are going to contribute to a greater profitability.
Operating Expenses and Marketing Spend
The operating costs of the e-commerce enterprises usually encompass:
Digital Marketing: Paid advertisements, social media and influencer agreements.
Technology Costs: Hosting and other platform payment, software subscriptions.
Logistics and Customer Service: Support Staff, delivery, warehousing.
The financial models can be used to predict both the increase in costs as growth and the impact of marketing expenditure on customer acquisition and retention.
Why it counts: It is important to have an appropriate expense model in place that will be profitable in terms of marketing investment and will make operations profitable without negating on the margins.
Cash Flow Management
The e-commerce cash flow is of great concern because of enciacking stock, delivery fees and the cyclical nature of the sales. The estimation of cash inflows and outflows allows the businesses to:
Determine possible liquidity deficiencies.
Make inventory orders in advance of high seasons.
Agree with suppliers and Korean shipping partners on payment terms.
Why it is important: With good cash flow management, there is reduced chances of errors caused by stockouts, late payments and disruption of operations.
Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis
E-business markets are unstable. Scenario modeling enables the business to test the assumption that:
Changes in conversion rates.
Rising shipping costs.
Change in customer acquisition cost (CAC).
The sensitivity analysis would also point out the strongest varying variables that influence the profitability and cash flow.
Why it is important: Being ready to face various situations allows making sure that e-commerce companies can be flexible, reduce risks, and make decisions in a more efficient manner even in times of uncertainty.
Funding and Investment Planning
Financial modeling Singapore assists e-commerce initiators to decide what funds to raise capital to acquire inventory, marketing and platform development. The founders are able to estimate the dilution, interest payable, and ROI to the investors by simulating equity, debt or hybrid financing solutions.
Why it is important: Explicit financial models enhance the confidence of investors and provide a basis on how to scale, join new markets or roll out new products.
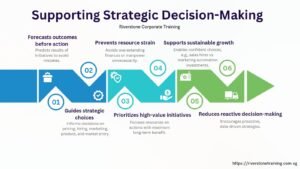
Strategic Decision Support
In addition to figures, a powerful financial model will guide core strategic decisions:
Choosing products and prices.
Channel division of marketing.
Inventory control and logistics strategy.
Penetration of new directions, markets.
Why it is important: The Transparency of financial data applied in strategy minimizes guesswork as well as focuses on the high impact projects, and enhances the competitiveness in the long term.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Growth with Financial Modeling
An online commerce financial investment plan is not a simple device, it is a plan. It directs the decision-making process, investor reporting, as well as articulating a business to counter the presence of market volatility. Through a reasonable projection of revenues, expenses, and flow of cash, as well as strategic options, e-commerce founders are capable of influential decisions marked by short term achievement and long term expansion.
Financial modeling converts data to action heights, which allows e-commerce firms to grow at an efficient level, invest sensibly and establish sustainable success within a volatile marketplace.