Amazing DCF Valuation Deep Dive: Unlevered Cash Flow, Discount Rate & Terminal Value
Amazing DCF Valuation Singapore Deep Dive: Unlevered Cash Flow, Discount Rate & Terminal Value
Introduction: Why DCF Matters
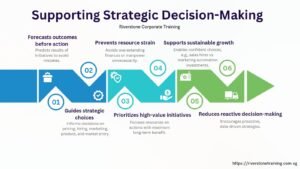
One of the best ways of establishing the intrinsic value of a company is by use of discounted Cash flow (DCF) valuation. In contrast to the market multiples that only compare a firm with its peers, DCF offers a forward looking method because it determines the present value of future cash flows that are expected to occur. That is why it is particularly useful when it comes to investors and managers who want to have a company-specific evaluation instead of trademark valuation Singapore references.
The key elements of DCF valuation Singapore to be emphasized by the decision making on DCF are to consider Unlevered Free Cash Flow (UFCF), the Discount rate, and the Terminal Value. All these are the building blocks of proper valuation, which will make financial analysis go beyond the superficial measures of financial analysis to encompass long-term growth, risk, and sustainability.
Unlevered Free Cash Flow (UFCF) – Measuring Core Business Value
Unlevered Free Cash Flow illustrates the amount of cash produced by the fundamental operations of a business and it can be availed to all financial providers of any business, both debt and equity, before financing charges.
Key points about UFCF:
Financing characteristics stripped effect -Concentrates on business performance, and not on capital structure.
Computed as: EBIT (1-Tax rate) + Depreciation and amortization- Capital expenditures+ unit Targets of changing working capital.
Reasons: Gives an unbiased picture of cash making, therefore, companies are similar despite leverage.
Managerial wisdom: Discovers real working strength and business model sustainability.
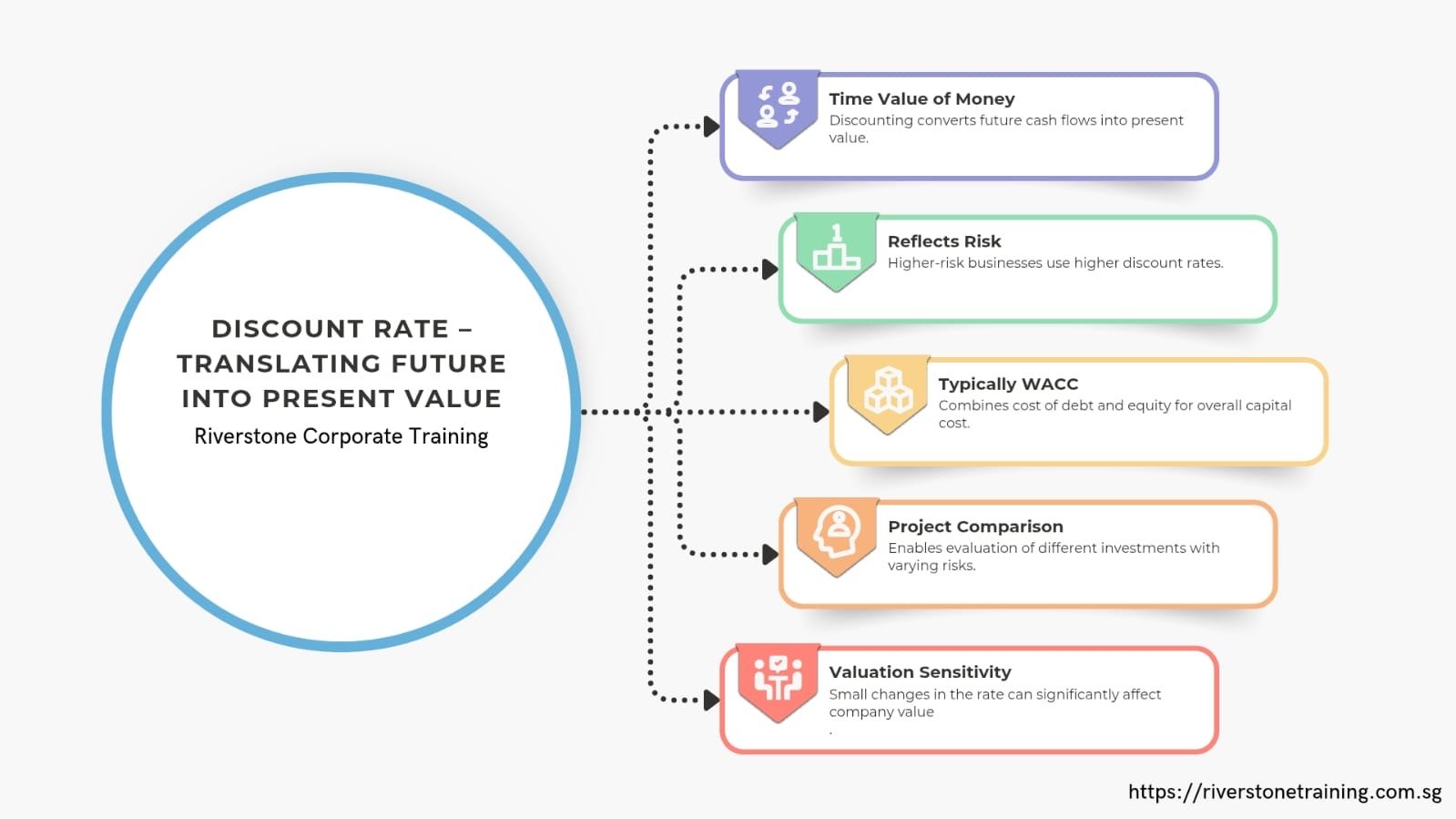
Discount Rate – Translating Future into Present Value
This is because money is worth more today than it will be tomorrow, therefore money ought to be discounted back to the present value. Discount rate indicates the time value of money as well as the riskiness of the cash flows.
The most significant issues around discount rate are:
Normally WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital): This is a combination of cost of debt and the cost of equity.
Risk-adjusted: Greater risks businesses prescribe greater discounts.
Strategic use: Assists in the comparison of various projects or acquisitions that have a varied risk-return profile.
Lesson learnt in leadership: Even a minor adjustment of the discount rate can lead to a large reinvention in valuation and one should be cautious to implement assumptions.
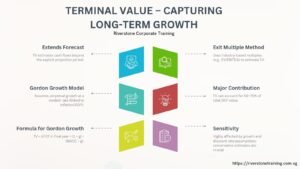
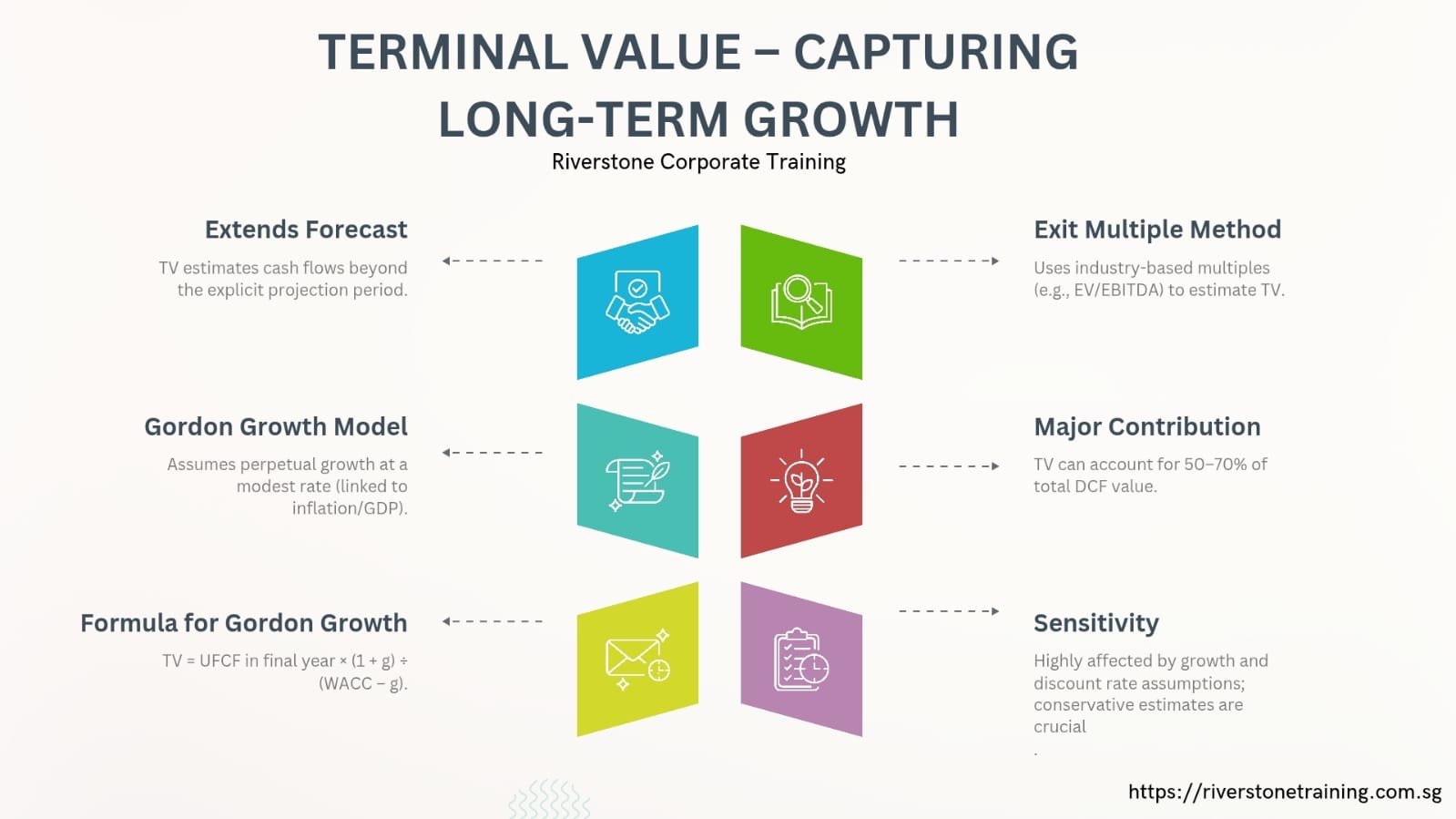
Terminal Value – Capturing Long-Term Growth
DCF models do not predict the cash flow in the long-term. Analysts alternatively rely on Terminal Value (TV) to bring an estimated value of all future cash flows past the explicit forecast period.
Two common approaches:
Gordon Growth Model: Process presupposes continuous growth at a small rate (in case with inflation, with the growth of GDP, etc.).
TV = UFCF in final year × (1 + g) / (WACC – g).
Exit Multiple Method: It uses a valuation multiple (e.g., EV/ EBITDA ) which is computed using the industry standards.
Why it matters:
Terminal Value Average values add 5070% of total DCF value.
Ability to grow and make discount assumption hedges, accuracy and conservative estimates are mandatory.
Helps adopt long term competitive edge or market positioning.
Bringing It Together – The DCF valuation Singapore Equation
After the determination of Unlevered Free Cash Flow (UFCF), discount rate, and terminal value, all these are put together, and they are used to calculate the value of the entire business. The basic formula is:
DCF Value = Present Value of Future Projected UFCFs + Present Value of ending Value.
The given calculation gives the Enterprise Value (EV) of the company, which is the overall value of operations not related to capital structure. Based on this EV, net debt and also on the preferred equity together with other claims are property adjusted to calculate the Equity Value which is the amount that is attributed to shareholders. Lastly, the Equity Value, on division with the number of outstanding strikes, will result in the intrinsic value of a share which will provide the investors an approximate view of the worth of the stock in the future.
Under this overall method, DCF encompasses both the short-term operations efficiency and long-term growth prospects. It enables decision-makers to determine areas in which a market price will meet intrinsic value which would aid in investment, acquisition or strategic financing decisions. Used intelligently, this approach can turn complex financial projections into shareholder and action-based information to both the shareholders and the management.
Conclusion: Turning Analysis into Strategic Insight
DCF estimation is an effective and delicate process that provides a complex system to theoretically approximate intrinsic value when determining its value. By making Discussion focus on Unlevered Free Cash Flow, a properly motivated Discount Rate, and critical estimation of the Terminal Value, leaders will be able to determine whether businesses, projects or acquisitions do make a long term value. The choice of each component is to be evaluated with critical attention to the fact that minor shifts might provide substantial differences to the outcomes.
DCF is more than a financial modeling DCF Valuation when implemented in a strategic way, it is a strategic design. It also assists leaders to evaluate sustainability, stress-test risks and reveal growth opportunities. DFS is more than a valuation technique because it empowers the organizations with an eyeglass insight-turning numbers into actionable data which would toughen the organization, enhance strategy, and create enduring stakeholder belief.